- Negative externalities occur when the consumption or production of a good causes a harmful effect to a third party. 当一种商品的消费或生产对第三方造成有害影响时,就会出现负外部性。

Examples of negative externalities 负外部性的例子
- Loud music 大声的音乐. If you play loud music at night, your neighbour may not be able to sleep. 如果你在晚上播放大声的音乐,你的邻居可能无法入睡。
- Pollution 污染. If you produce chemicals and cause pollution as a side effect, then local fishermen will not be able to catch fish. This loss of income will be the negative externality. 如果你生产化学品并造成污染的副作用,那么当地渔民将无法捕鱼。这种收入的损失将是负面的外部性。
- Congestion 拥堵. If you drive a car, it creates air pollution and contributes to congestion. These are both external costs imposed on other people who live in the city. 如果你驾驶汽车,就会造成空气污染,并导致拥堵。这些都是强加给生活在城市里的其他人的外部成本。
- Building a new road 修建一条新路. If you build a new road, the external cost is the loss of a beautiful landscape which people can no longer enjoy. 如果你修建一条新路,其外部成本是失去了一个美丽的景观,人们无法再享受。
The externalities of driving a car to work 开车上班的外部因素
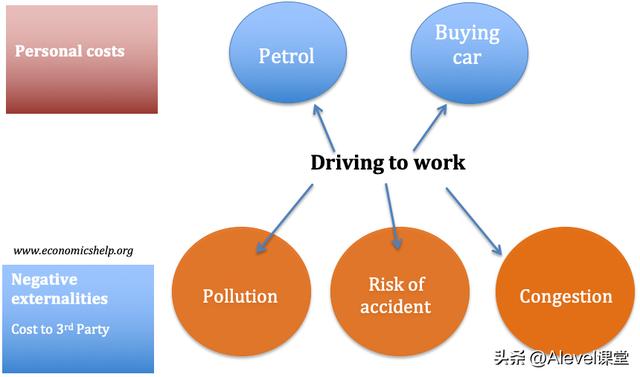
- The personal cost of driving are buying car, petrol, your time 驾驶的个人成本是买车、汽油和你的时间。
- The negative externalities are – pollution to other people, possible accident to other other people, and time other people sit in traffic jams 负面的外部因素是–对其他人的污染,对其他人可能发生的事故,以及其他人坐在交通堵塞中的时间。
Social cost 社会成本
- Social cost is the total cost to society; it includes both private and external costs. 社会成本是社会的总成本;它包括私人和外部成本。
- With a negative externality the Social Cost > Private Cost 在负外部性的情况下,社会成本>私人成本
Negative production externality 负的生产外部性
- When producing a good causes a harmful effect to a third party. Therefore the social cost is greater than the private cost. 当生产一种商品对第三方造成有害影响时。因此,社会成本大于私人成本。
Examples of negative production externalities 负生产外部性的例子
- Burning coal for energy creates pollution. 燃烧煤炭作为能源会造成污染。
- Producing conventional vegetables with pesticides causes carcinogens to get into the environment. 用杀虫剂生产常规蔬菜会导致致癌物进入环境。
- Producing beef in South America involves cutting down Amazon rainforest, which has an impact on global climate and local environment 在南美生产牛肉需要砍伐亚马逊雨林,这对全球气候和当地环境都有影响。

- Because of the external costs the social marginal cost is greater than the private marginal cost. 由于外部成本的存在,社会边际成本要大于私人边际成本。
- In a free market, producers ignore the external costs to others. Therefore output will be at Q1 (where demand = Supply). 在一个自由市场中,生产者忽略了他人的外部成本。因此,产出将在Q1(需求=供给)
- This is socially inefficient because at Q1 – SMC> SMB 这是社会无效率的,因为在Q1 – SMC> SMB
- Social efficiency occurs at Q2 where Social marginal cost = Social marginal benefit 社会效率发生在Q2,社会边际成本=社会边际收益
The red triangle is the area of deadweight welfare loss. It indicates the area of overconsumption (where SMC is greater than PMC) 红色三角形是致命福利损失的区域。它表示过度消费的区域(SMC大于PMC的地方)
Negative externality of consumption 消费的负外部性
This occurs when consuming a good causes a harmful effect to a third party. In this case, the social benefit is less than the private benefit. 当消费一种商品对第三方造成有害影响时,就会出现这种情况。在这种情况下,社会利益小于私人利益。
Examples of negative externalities of consumption 消费的负外部性的例子
- Consuming alcohol leads to an increase in drunkenness, increased risk of car accidents and social disorder. 饮酒导致醉酒率上升,车祸风险增加,社会秩序混乱。
- Consuming loud music late at night keeps your neighbours awake. 深夜消费高声音乐,使邻居无法入睡。
- Consuming cigarettes causes passive smoking to others in the vacinity. 消耗香烟会使周围的人被动吸烟。
Diagram of negative externality in consumption 消费中的负外部性图示
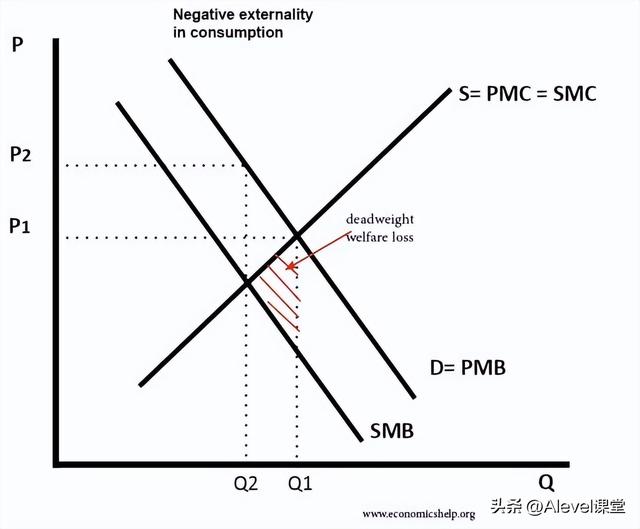
- In a free market, we get Q1 output. But at this output, the social marginal cost is greater than the social marginal benefit. 在一个自由市场中,我们得到Q1的产出。但在这个产出中,社会边际成本大于社会边际收益。
- The red triangle is the area of dead-weight welfare loss. 红色三角形是死量福利损失的区域。
- Social efficiency occurs at a lower output (Q2) – where social marginal benefit = social marginal cost. 社会效率发生在一个较低的产出(Q2)–社会边际效益=社会边际成本。
Implications of negative externalities 负外部性的影响
If goods or services have negative externalities, then we will get market failure. This is because individuals fail to take into account the costs to other people. 如果商品或服务具有负外部性,那么我们将得到市场失灵。这是因为个人没有考虑到其他人的成本。
To achieve a more socially efficient outcome, the government could try to tax the good with negative externalities. This means that consumers pay close to the full social cost. 为了达到一个更有效的社会结果,政府可以尝试对具有负外部性的商品征税。这意味着消费者支付接近全部的社会成本。
Economists on negative externalities 经济学家对负外部性的看法
Arthur Pigou 1920 introduced the concept of externalities in The Economics of Welfare. Pigou used the example of alcohol having external costs, such as creating more demand for police and health care. Arthur Pigou 1920年在《福利经济学》中提出了外部性的概念。皮古用酒精具有外部成本的例子,如对警察和卫生保健产生更多需求。
In 1975 William Baumol and W. Oates provided a comprehensive review of the literature on externalities in Theory of Environmental Policy. In particular, they applied economic concepts of externalities to the emerging issue of environmental costs. For example, in 1975, they mentioned some of the environmental costs which were considered to be pressing. 1975年,William Baumol和W. Oates在《环境政策理论》中对关于外部性的文献进行了全面的回顾。特别是,他们将外部性的经济概念应用于新出现的环境成本问题。例如,在1975年,他们提到了一些被认为是紧迫的环境成本。
a. Disposal of toxic wastes, 有毒废物的处理
b. Sulfur dioxide, particulates, and other contaminants of the atmosphere, 二氧化硫、颗粒物和大气的其他污染物
c. Various degradable and nondegradable wastes that pollute the world’s waterways, 污染世界水路的各种可降解和不可降解的废物
d. Pesticides, which, through various routes, become imbedded in food products, 杀虫剂,通过各种途径,浸泡在食品中
e. Deterioration of neighborhoods into slums, 社区恶化为贫民窟
f. Congestion along urban highways, 城市公路沿线的拥堵
g. High noise levels in metropolitan areas 大都市地区的高噪音水平










